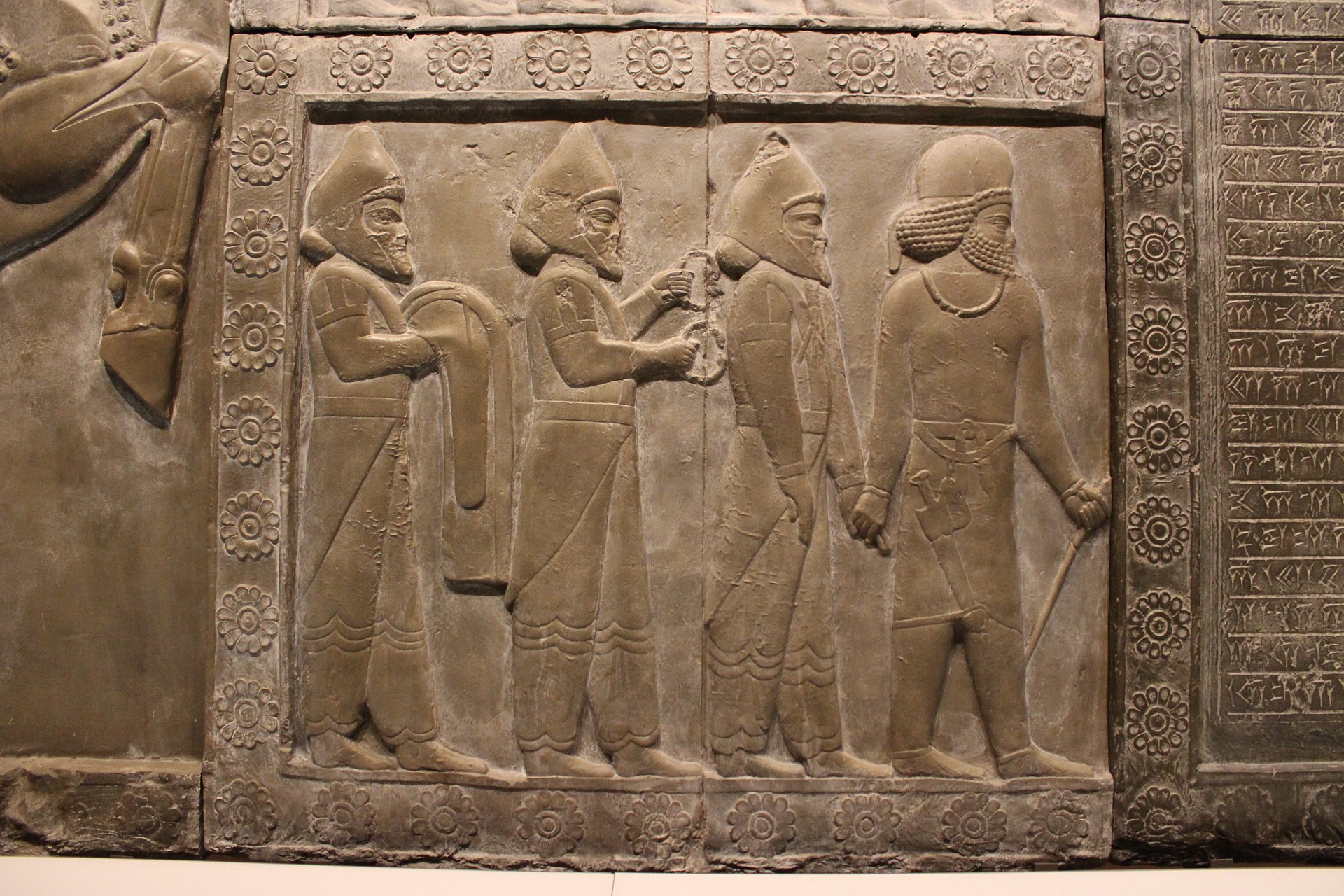
The laws of the first civilizations, such as those of ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, provide insight into the social and legal systems of some of the earliest known human societies. These civilizations developed these laws to address property ownership, trade, and crime, reflecting these early people’s cultural and political values.
One of the most well-known sets of ancient laws is the Code of Hammurabi, created by the Babylonian king Hammurabi in the 18th century BC. When Hammurabi was still young, his father abdicated the throne, and Hammurabi succeeded him as king. At the time, Babylon was a relatively small and weak city-state surrounded by more prominent and influential kingdoms. Hammurabi realized he needed to expand his kingdom and build a strong military to protect it from its enemies. Hammurabi began a series of military campaigns to expand Babylon’s territory. In addition to his military and economic achievements, Hammurabi is perhaps best known for creating the Code of Hammurabi. This legal code was engraved on a large stone monument and placed in a public location where everyone could see it. The laws covered many topics, including family, property, and criminal law.
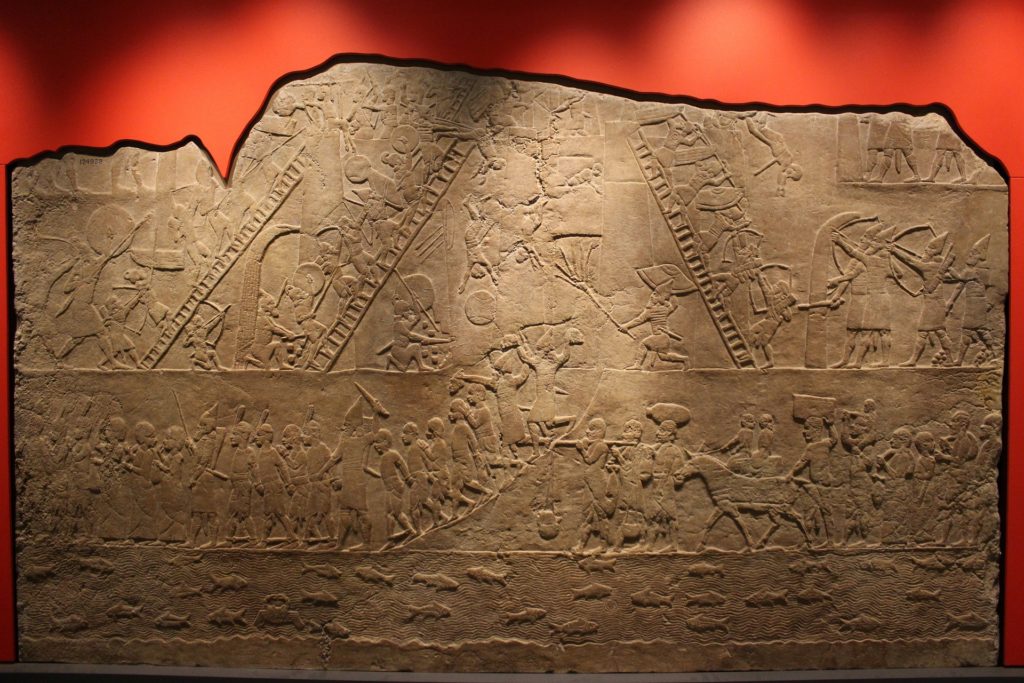

The Code of Hammurabi was significant because it was one of the first legal codes to be written down and preserved. The 282 laws engraved on a large stone pillar address various issues, including property rights, marriage and divorce, and criminal behavior. The code established a strict system of justice that emphasized retribution and punishment, with different punishments prescribed for different crimes based on the status of the victim and the perpetrator. It was also one of the most comprehensive legal codes of its time and has had a lasting impact on the development of legal systems worldwide. The basis of this code is the principle of “an eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth,” which meant that punishments were proportional to the crimes committed.
In ancient Egypt, the laws were less codified than in Mesopotamia, but examples of legal documents have survived. One such document is “The Eloquent Peasant,” a narrative poem describing a legal dispute between a peasant and a corrupt official. The poem highlights the importance of justice and fairness in Egyptian society and demonstrates the legal protections available to its lowest social classes.
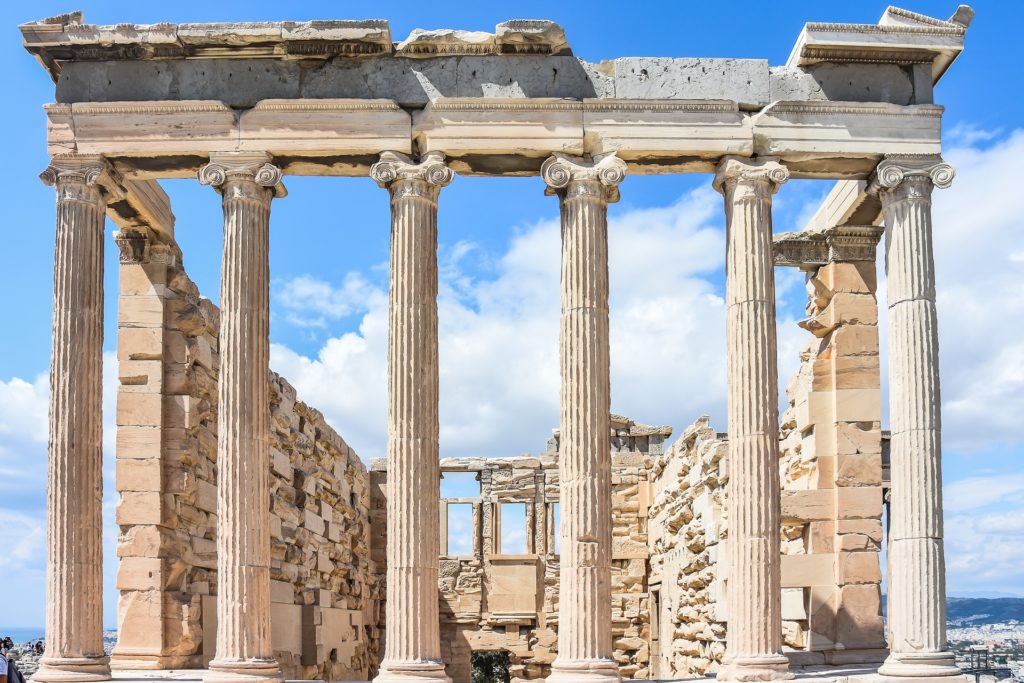
Another early civilization with a well-developed legal system was Ancient Greece. The Greek city-states had different legal traditions and practices but shared a commitment to the rule of law and the idea of justice. Athens is particularly well-known for its legal system, which included juries and the concept of a fair trial. The ancient Greeks developed their legal system over several centuries, and it is not easy to attribute it to a single individual. However, the famous Athenian lawmaker Solon made some of the most significant contributions to the development of Greek law.
Solon was an Athenian statesman who lived in the 6th century BCE. He is known for his role in laying the foundation for Athenian democracy and for his legal reforms, which aimed to address social inequality and reduce tensions between the city’s various factions. Among his most significant legal reforms was the cancellation of all debts and the prohibition of debt slavery, as well as the establishment of a system of courts that provided greater access to justice for all citizens.
Other notable figures who contributed to the development of Greek law include Draco, who created a written legal code in Athens in the 7th century BCE, and Lycurgus, the legendary Spartan lawgiver credited with establishing the strict and highly regimented legal and social system of Sparta.
The development of Greek law was a complex and ongoing process, with many different individuals and institutions contributing to its evolution over time. Today, the legacy of ancient Greek law continues to be studied and celebrated as an essential part of Western legal and political tradition.

Various factors, including religion, social customs, and political power, influenced the laws of the first civilizations. Many of these laws were harsh and punitive, reflecting these early societies’ unequal power dynamics. However, they also represent an essential step in developing legal systems and demonstrate the human desire for order and justice.
The laws of the first civilizations provide a captivating glimpse into the social and legal systems of some of the earliest known human societies. While these laws were often harsh and unequal, they also demonstrate the value of justice and fairness in ancient societies and the ongoing human quest for order and stability.